
The cloud storage of the fitness program Fitify exposed hundreds of thousands of files to the network. Some of them were photos of users that they would rather not share.
The Fitify service forgot to secure Google’s own cloud storage and thus caused free access up to 373 thousand accumulated files. 138 thousand of them turned out to be private photos of the service’s users, in which they recorded changes in their bodies as a result of sports activities. Usually, such photos are taken with a minimum of clothing, so it is not surprising that the leak quickly attracted attention.
It is known that 13 thousand files were distributed via AI trainer and another 6,000 were labeled as «3D body scan data» with images and some AI data. Private data was available without passwords or keys, and the situation could have been even worse if the vulnerability had been exploited. Through the «window, it was possible to gain access to even more sensitive user data.
But fortunately, this did not happen, and the Cybernews research team that discovered the vulnerability quickly notified Fitify employees of the problem. After that, public access to the storage was closed.
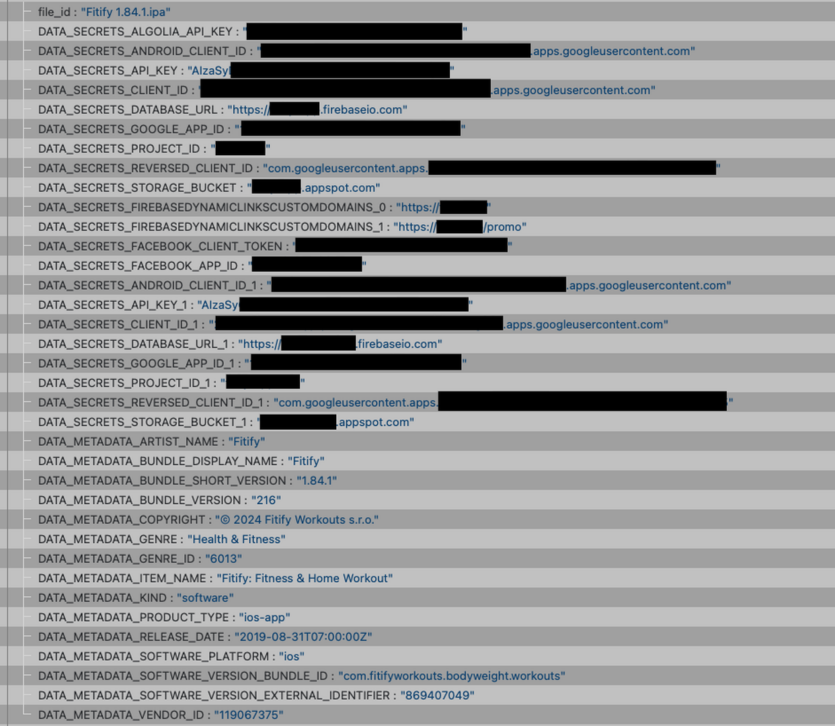
The leak showed that anyone could get data from Fitify without any difficulty. The main reason was the lack of encryption in the storage mode. The company also provides fairly easy access to such important information as Android Client ID, Google Client ID, Google API Key, and many others. And, for example, knowing the first two, you can easily fake legitimate instances of the application and read a lot of user data, including access to social networks.
The Cybernews team also conducted additional research, downloading 156 thousand different iOS applications from the Apple App Store (about 8% of all available). As a result, it turned out that 71% of them had at least one leak of user information. The average rate was 5.2.
As a result, Cybernews employees stated:
«After investigating the vulnerabilities, we found credentials that could potentially be used to access customer data and the application’s server infrastructure.The research also shows that misconfigured cloud access management was not the only mistake made by application developers. Numerous API keys and sensitive data were often present in the front-end of the application»
To prevent the above problems, the Cybernews team recommends:
- Configure built-in cloud storage authentication mechanisms so that access to cloud storage is limited to employees and systems that are authorized to access the stored data.
- Get rid of compromised credentials and create new ones. Securely store them on the company’s servers.
- View access control settings for open endpoints.
- Conduct more frequent audits.
- Update applications more frequently to make them compatible with the new, more secure infrastructure.
Source: Cybernews

Spelling error report
The following text will be sent to our editors: