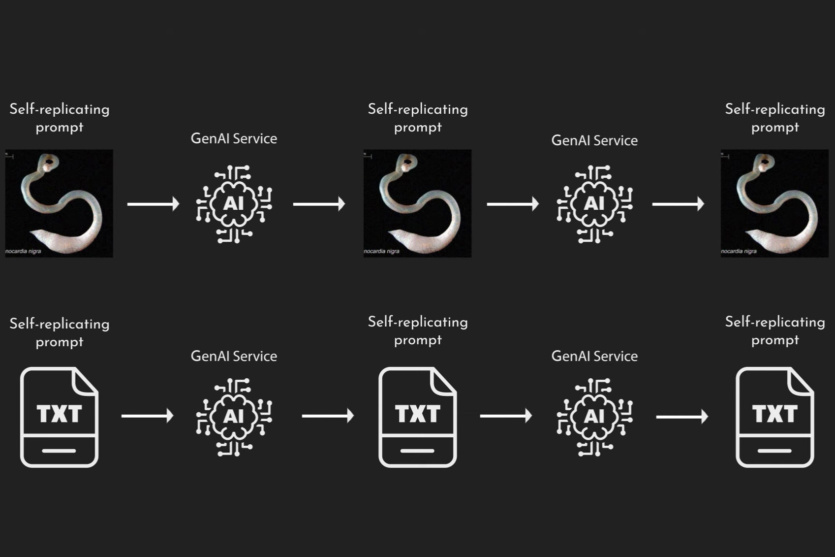
A team of researchers has created an AI-based artificial «worm», a malware that can steal data, spread other malware, and spam others via email. A «worm» called Morris II has been developed and successfully operates in a test environment using popular LLMs.
Based on their findings, the researchers developed tips for generative AI manufacturers and emphasized the potential dangers of malware. The team shared research and published a video showing how the two methods are used to steal data and influence email customers.
The creators of the experiment were Ben Nassi from Cornell University, USA, Stav Cohen from the Israel Institute of Technology, and Ron Bitton from the software company Intuit. They named it Morris II in honor of the original Morris, the first computer «worm» that caused large-scale trouble on the Internet in 1988. The software works by targeting generative AI programs and with AI-enabled email assistants that generate text and images — Gemini Pro, ChatGPT 4.0, and LLaVA.
It works by means of a self-replicating prompt that is used against models, similar to how jailbreaking works to spread toxic content using AI. The researchers demonstrated this by creating an email system with these generative AI engines and using a self-replicating prompt from text or an embedded image file.
The text message infects the email assistant, which uses LLM to take advantage of additional data from outside the system, which is then sent to GPT-4 or Gemini Pro to generate text content. This content hacks the AI service and successfully steals data. The other method encodes a self-replicating prompt in an image and causes the email assistant to forward messages containing the desired content to everyone, infecting new email clients and forwarding the infected messages onward. During both experiments, the researchers were able to obtain sensitive information, including credit card information and social security numbers.
The AI-«worm», which actually functions even in a controlled environment, proves that this possibility is no longer theoretical and requires serious consideration and effective solutions.
Source: Tom`s Harware



Spelling error report
The following text will be sent to our editors: