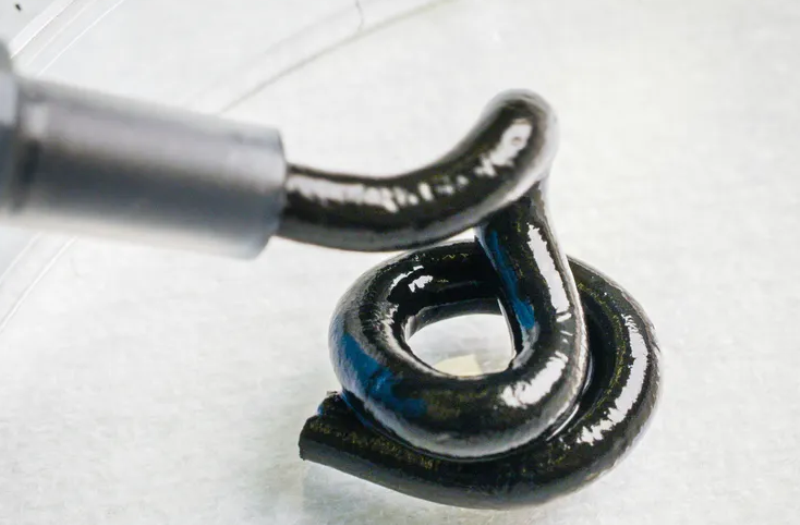

Swedish scientists from the University of Linköping created a soft battery with liquid electrodes.
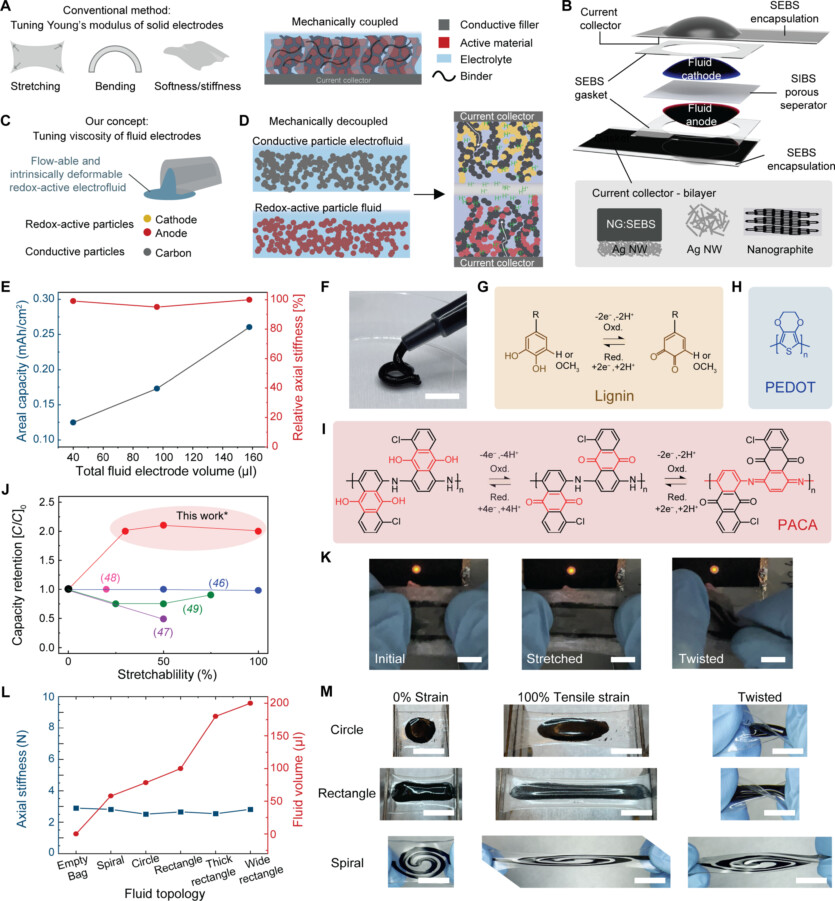
Today, batteries are the power source for most electronic devices, from smartphones to smartwatches, laptops, and electric cars. Batteries are made of solid materials and have a certain volume. However, Swedish researchers set out to create a flexible battery that could be molded into any shape and could even be printed on a 3D printer. Their design uses liquid electrodes to conduct electric current from the anode to the cathode.
«Batteries are the largest component of all electronics. Today, they are robust and quite bulky. But with a soft and flexible battery, there are no design restrictions. It can be integrated into electronics in a completely different way and adapted to the user. The texture is a bit like toothpaste. The material can, for example, be used in a 3D printer to give the battery any shape you want», — notes the co-author of the study Ayman Rakhmanudin.
The Swedish developers emphasize that previous attempts to create soft stretchable batteries relied on mechanical features, among other things, sliding joints, or required expensive and rare materials, the processing of which leads to environmental pollution. The success of the new development was the creation of liquid electrodes.
Larger batteries have a higher electrical capacity, but also thicker — and therefore stiffer — electrodes. According to Rakhmanudin, he and his colleagues were the first to prove that battery capacity does not depend on stiffness.
The researchers emphasize that they tried to circumvent the limitations of previous developments based on liquid metals, which eventually became solid. In their battery, the scientists used plastics capable of conducting electric current, called related polymers, as well as lignin, which is a waste product of the paper industry. Created a battery can withstand up to 500 discharge-charging cycles, even if it is stretched to twice its original length The materials used in this battery are not scarce or expensive.
«Since the materials in the battery are compounds of polymers and lignin, there is an abundance of this raw material. By repurposing a by-product such as lignin into a valuable commodity such as battery material, we are contributing to a more circular model. Thus, it is a sustainable alternative»,— emphasizes the lead author of the study, Researcher at the Laboratory of Organic Electronics, University of Linköping Mohsen Mohammadi.
As noted by Ayman Rakhmanudin, the team of scientists managed to prove the viability of the soft battery concept, but work is needed to improve the performance of this device. Currently, the voltage is only 0.9 V. Standard AA batteries have a voltage of 1.2 to 1.5 V, and most smartphones operate at 3.7 to 4.2 V.
The researchers plan to consider using other chemical compounds to increase the voltage. However, the development already opens the door to designing completely new battery-powered devices.
Up to 6000 cycles: a Ukrainian startup has developed an eco-friendly alternative to Li-Ion batteries
The results of the study were published in the journal Science
Source: Gizmodo

Spelling error report
The following text will be sent to our editors: