
In the previous article we have reviewed Bluetooth audio codecs used to listen to music. However, codecs are only a small part of the «iceberg» of technologies that are needed not only to play music. That’s why today we’re going to look at Bluetooth profiles, without which we couldn’t even hear our loved ones, and we couldn’t see your heart rate data on a fitness tracker.
Content
What is a Bluetooth profile?
Bluetooth profile — is a set of functions that define how Bluetooth devices interact with each other. That is, how they are connected, signal each other, and transfer data between them. All the profiles listed in the respective section below are designed to perform different functions. For example, one profile (A2DP) is used to play music in a headset, while a completely different profile (HSP or HFP) is used to transmit your voice and the voice of the person you are talking to.
Connection channels between Bluetooth devices
Since the two devices are not physically connected to each other, it is necessary to ensure that they are connected to each other. Therefore, two types of channels are used for transmission:
- ACL or Asynchronous Connection-Less — is used to transfer data without the need for guaranteed real-time delivery;
- SCO or Synchronous Connection-Oriented — used to transfer data in real time, i.e. with minimal delay.
ACL connection is characterized by the following features: support for two-way data exchange, correction of potential transmission errors, and variable delays. ACL is used in a wide range of applications: file transfer via Bluetooth, audio streaming, interaction with Bluetooth keyboards and mice.
Unlike ACLs, SCO connections require a clearly defined time frame to ensure minimal delays when using the profile. First of all, this is necessary for voice transmission during a telephone conversation. That’s why there is no error correction function in situations where the other party could not hear you well.
Roughly speaking, the use of SCOs is necessary for fast information transfer, while ACLs are for quality assurance.
Here is a brief comparison table of both types of data transmission. As you can see, it’s pretty clear when and how to use one or the other type of channel.
| ACL | SCO | |
| Types of data to be transferred | Normal files, audio, device management control | Voice (phone calls) |
| Synchronization | Asynchronous | Synchronous (fixed time intervals) |
| Repeat the program | Possible | Actually impossible (to avoid delays) |
| Delay | Variable | Stably low |
Bluetooth data exchange mechanisms
Data transfer between devices comes in two similar variations:
- Bluetooth BR/EDR or Basic Rate / Enhanced Data Rate;
- Bluetooth Low Energy. The abbreviation BLE or Bluetooth Smart is often used.
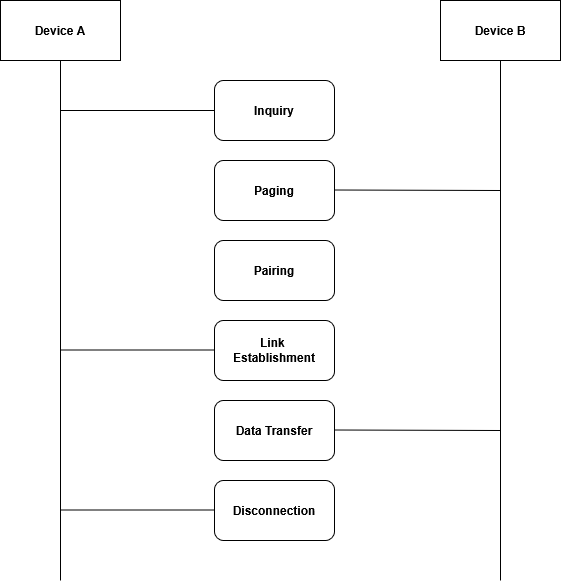
Let’s start with BR/EDR and, for the sake of clarity, the diagram below. First, Device A (smartphone) must somehow find Device B (headphones). To do this, you need to start the procedure Inquiry in which one of the devices initiates a search for «its neighbors» using special data packets. In our case, the role of the initiator is played by Device A. After detection, the initiator sends the corresponding Paging to connect and the process begins Pairing with setting the level of trust, verification code, authentication and, if necessary, encryption. After that, you can perform Link Establishment through logical channels and define device roles: Master (master, connection initiator, Device A) or Slave (secondary, Device B).
Next, the data transmission channels mentioned earlier come into play. Namely, you choose between an ACL or SCO connection. As mentioned above, different methods need to be used for different purposes: transferring audio or files (ACL) or voice during calls (SCO).
Next, we’ll see something similar to OSI model, which uses stacks of internal Protocols and Layers, including:
- Profiles that describe the logic of interaction between devices: A2DP, AVRCP, OBEX, and others. In the next section, we will get to them;
- Service level — detection and, if necessary, emulation of supported protocols of the higher level. For example, SDP (Service Discovery Protocol);
- Management via L2CAP transmission channels;
- Baseband and Link Manager to manage connections, master/slave roles, and power consumption;
- Physical level (Physical Layer), which will transmit everything you need over the radio channel.
Then it goes by itself Data Transfer between Devices A and B according to the required protocol. If it is necessary to transmit the sound of a user’s track from Device A, then the digital data is transferred to A2DP (this is where encoding and decoding takes place), through the Bluetooth stack to L2CAP, divided into parts and sent via ACL over the radio channel. Device B receives this data in its internal program and starts playing it to the speakers.
Of course, after all these actions, there comes a moment Disconnect the connection which can be initiated by either device. At this point, the logical and physical transmission channels are disabled. To increase further connection speed, they must remain paired (be aware of each other).
Regarding the fairly new Bluetooth Low Energy standard, we can say that the mechanisms are similar, but they use different protocols and terminology. That’s why we have a big disadvantage — there is no compatibility between devices of both generations. However, there is a big plus — reduced power consumption due to the new mode of operation. After direct operation, the still connected devices significantly reduce the «contacts» between them, which saves the batteries of both devices. This is especially true for a variety of smartwatches, business trackers and hearing aids (TMAP profile support).
Bluetooth profiles
Let’s move on to the list of Bluetooth profiles themselves. Each of them is designed to fulfill a specific purpose. By viewing the profiles of the device you have chosen, you can immediately understand its potential functionality. We will also say a few words about them.
Profile A2DP (Advanced Audio Distribution Profile), is perhaps the most famous of all profiles in the world. It is thanks to him that humanity has been listening to music or podcasts in their wireless headphones for many years. It supports many standard codecs, such as SBC, AAC. However, as you may not have noticed, the profile works only in one direction: from Master (smartphone on which the track is running) to Slave (headphones in which the track is playing).
If you need to pause the song, switch to another one, or increase/decrease the volume, at this point the profile AVRCP (Audio/Video Remote Control Profile) gets to work. As the name implies, it also allows you to control when watching videos.
But for calls, another well-known profile from ancient times is used — HFP or Hands-Free Profile. It is used for voice calls, dialing, accepting or rejecting calls, checking signal strength, and more. Its most important function is to transmit the sound of the call itself.
In 2022, the new profile mentioned above was introduced to replace A2DP, HFP, and AVRCP — TMAP (Telephony and Media Audio Profile). As you can see, it should combine a profile stack that will ensure compatibility between next-generation Bluetooth LE devices. It supports the new LC3 codec, which is also supposed to replace SBC and AAC. As this profile becomes more widespread in the world (hardware support for Bluetooth version 5.2 and higher is required), it may happen that your cool and expensive headphones (bought more than 5 years ago) simply won’t work with a new smartphone. However, this is unlikely to happen in the near future.
In the old days of push-button phones, address book contacts were transferred using PBP (Phone Book Access Profile). Nowadays, it is not forgotten, because it is used to wirelessly connect a smartphone to a car and show contacts on a larger display.
Here are a few other important Bluetooth profiles that you use without even knowing they exist.
If HFP is used for voice calls, then who allows SMS/MMS and notifications to be sent to smartwatches or car displays? This is a job for MAP (Message Access Profile). To connect a mouse, keyboard, or gamepad via Bluetooth, you also need your own profile. Namely, HID or Human Interface Profile.
Do you remember when Sony Ericsson K750i and Siemens M65 used to transfer all kinds of music or images to each other’s phones? To perform this operation, profiles were used OBEX (Object Exchange) and OPP (Object Push Profile).
Perhaps you’ve encountered the problem of an urgent need for the Internet? You don’t have an Ethernet cable or home WiFi. But you have a smartphone with mobile Internet nearby. Why not create a Bluetooth hotspot between the two devices? This is the responsibility of PAN (Personal Area Networking Profile).
When working in grocery chains, label printing devices are often used. These and other products (POS terminals, automotive industry) use COM ports in their operations. Profile SPP (Serial Port Profile) allows you to emulate this port via Bluetooth connection, thereby replacing the cable connection.
Profile SIM Access Profile (SAP or rSAP) allows devices built into the car with a GSM transmitter to connect to the SIM card in a Bluetooth-enabled smartphone. This eliminates the need for a separate SIM card and allows you to start using the car’s external antenna.
If you wear fitness trackers or other devices to track your health, they also have their own profile. More precisely, there are several of them: FMP (Fitness Machine Profile), HDP (Heart Device Profile), HRP (Heart Rate Profile) and PAMP (Physical Activity Monitor Profile). Each of them is necessary for different user activities.
As you can see, there are many Bluetooth profiles for a wide variety of user tasks. Some of them are already many years old (the first version of A2DP was officially adopted in May 2003), but they still fulfill their main function — to please users.



Spelling error report
The following text will be sent to our editors: